In treating prostate cancer, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) offers demonstrated patient benefits by accelerating radiation treatments, from the conventional five to nine weeks to a five-day treatment program, with comparable efficacy.
SBRT can increase the risk of side effects, particularly to the rectum. The shorter course of SBRT can increase radiation dose to the rectum, causing ulceration and rectal bleeding. To try to prevent these potential side effects, a new approach under investigation at Vanderbilt University Medical Center combines SBRT with an injectable hydrogel barrier (SpaceOAR by Augmenix, Inc.) used to minimize rectal exposure to radiation.
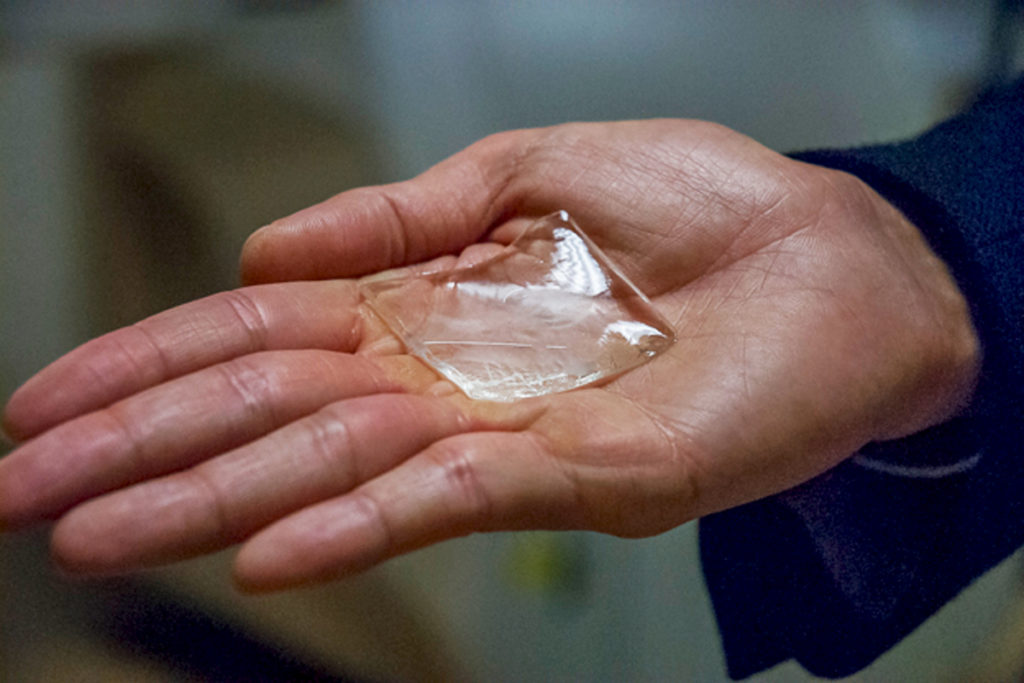
SpaceOAR is an FDA-approved, polyethylene glycol-based hydrogel that can be injected between the rectum and the prostate to push the rectum away from the prostate. It is injected during standard fiducial marker placement for radiation therapy with no additional visits required. Following treatment, the SpaceOAR gel is gradually absorbed, without need for an additional procedure.
Research on SpaceOAR
Studies using SpaceOAR with conventional radiation therapy for prostate cancer have shown reductions in rectal side effects including ulceration and post-procedure bleeding.
Newer studies, including one underway at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, are investing SpaceOAR’s efficacy in SBRT treatment for prostate cancer with promising initial findings.
“In addition to reducing rectal side effects… SpaceOAR may also reduce the risk of having erectile dysfunction or impotence after radiation treatments.”
“We’re collecting data to see, ‘Is there an improvement in the sexual and rectal side effects of men who get stereotactic radiation and get the SpaceOAR product?’” said Eric Shinohara, M.D., vice chair of radiation oncology at Vanderbilt. “In addition to reducing rectal side effects, observes Shinohara, “it appears that SpaceOAR may also reduce the risk of having erectile dysfunction or impotence after radiation treatments.” Shinohara also notes that SpaceOAR may mitigate some urinary side effects of prostate cancer SBRT.
Current Availability
At Vanderbilt, SpaceOAR is currently available off-trial for prostate cancer patients choosing standard radiation therapy or brachytherapy. Clinical trials investigating SpaceOAR for SBRT are ongoing at Vanderbilt.